Life Insurance Basics
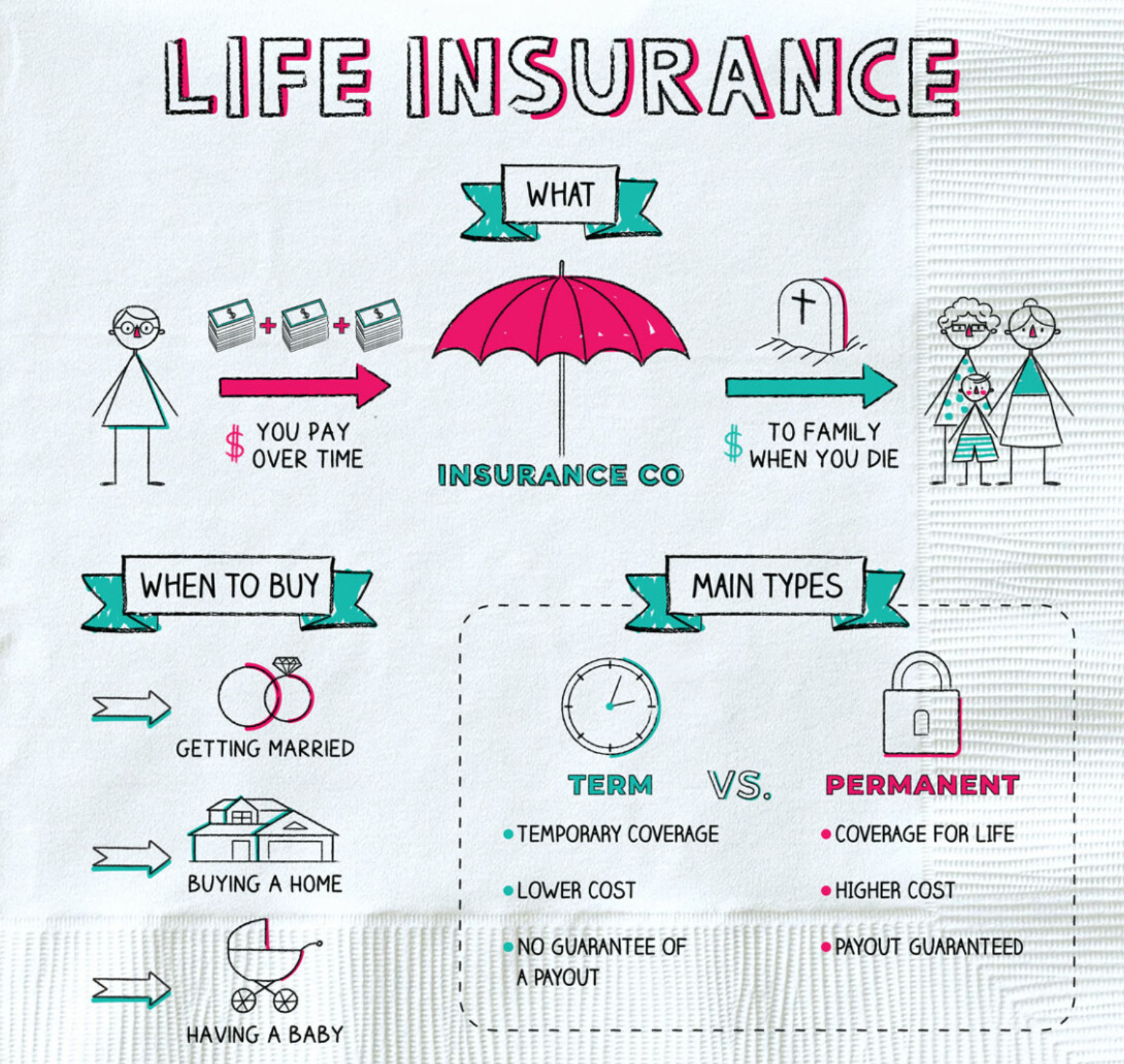
Life insurance is a type of insurance that provides financial protection to your loved ones in the event of your unexpected death. It pays out a lump sum of money to your beneficiaries, typically your family members, to help them cover expenses such as funeral costs, outstanding debts, or everyday living expenses.
To get life insurance, you typically start by paying regular premiums to an insurance company. The amount of the premium you pay depends on factors such as your age, health, lifestyle, and the amount of coverage you choose. In exchange for your premiums, the insurance company agrees to pay out a specified amount of money, known as the death benefit, to your beneficiaries upon your death.
There are several types of life insurance, including term life insurance, whole life insurance, and universal life insurance. Term life insurance provides coverage for a set period of time, usually between 10 and 30 years. Whole life insurance policies provides lifetime coverage and also has a savings component that can grow over time. Universal life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that offers more flexibility in terms of premiums and death benefits.
When you die, your beneficiaries will need to file a claim with the insurance company and provide proof of your death. If the claim is approved, the insurance company will pay out the death benefit to your beneficiaries. The death benefit is typically paid out tax-free and can be used for any purpose your beneficiaries choose.
Life insurance is not a pyramid scheme or a scam. It is a legitimate type of insurance that provides financial protection to your loved ones in the event of your unexpected death. The insurance company collects premiums from policyholders and invests the funds to ensure they have sufficient reserves to pay out the death benefits when they are needed. This is a legitimate and regulated industry that is subject to state and federal regulations, and insurance companies are required to meet specific financial and solvency standards to ensure they can fulfill their obligations to policyholders.
However, it’s important to note that not all life insurance policies are created equal. Some policies may have higher premiums or more limited coverage than others, so it’s important to research and compare different policies before choosing one that meets your needs. Additionally, it’s important to work with a reputable and licensed insurance agent or broker who can help you understand your options and select the right policy for you.
In addition, life insurance policies that have a savings component, such as whole life or universal life insurance, may allow policyholders to borrow or withdraw funds from the policy’s cash value to invest. It's important to note that borrowing or withdrawing funds from a life insurance policy can have tax implications and may affect the policy's overall performance.
Life insurance premiums are not tax-deductible. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) considers life insurance to be a personal expense, not a business expense, and therefore premiums paid for individual life insurance policies are not tax-deductible. This means that you cannot deduct the cost of premiums paid for your own life insurance policy on your federal income tax return.
However, there are some situations where life insurance premiums may be tax-deductible. For example, if you own a business and purchase life insurance for a key employee, the premiums may be tax-deductible as a business expense. Additionally, if you are self-employed and purchase a life insurance policy as part of a qualified retirement plan, you may be able to deduct the premiums as a business expense.
It's important to note that any death benefit paid out from a life insurance policy is generally not subject to federal income tax, meaning your beneficiaries will receive the full amount of the death benefit tax-free. However, there are some exceptions to this rule, such as if the policy was sold for a profit or the death benefit was paid out over time instead of as a lump sum.
Life insurance is an important financial planning tool that can provide peace of mind to you and your loved ones. It's recommended that you consider getting life insurance if you have dependents who rely on your income, such as children or a spouse. Life insurance can provide a financial safety net to ensure that your loved ones are taken care of in the event of your unexpected death.
In addition to having dependents, there are other factors to consider when deciding when to get life insurance. For example, if you have outstanding debts such as a mortgage or student loans, life insurance can help cover those debts in the event of your passing. Similarly, if you own a business or have a business partner, life insurance can be used to fund a buy-sell agreement in the event of one partner's death.
It's important to note that the cost of life insurance premiums typically increases with age, so it's generally more cost-effective to purchase life insurance when you are younger and in good health. However, it's never too late to purchase life insurance, and some coverage is better than none.
As always, it's important to consult with a qualified tax professional or financial advisor to fully understand the tax implications of life insurance policies and determine whether you may be eligible for any tax deductions or benefits.
In conclusion, life insurance is an essential financial tool that can provide peace of mind to you and your loved ones. By paying premiums, you can ensure that your beneficiaries receive a death benefit in the event of your unexpected passing. Life insurance can help cover expenses such as funeral costs, outstanding debts, and even provide financial security to your loved ones after you are gone. There are various types of life insurance policies available, each with its own unique features and benefits, so it's important to carefully consider your options and choose a policy that meets your specific needs. Overall, life insurance is a valuable investment that can help protect your family's financial well-being and provide a safety net for the future.